In the realm of construction and civil engineering, understanding the basics of aggregates is crucial for anyone seeking to build durable and sustainable structures. Aggregates are not just foundational elements; they play a critical role in defining the integrity and longevity of various infrastructural projects. This comprehensive overview will delve into what is aggregate, their essential characteristics, various types, and their pivotal role in construction.
What is Aggregate?
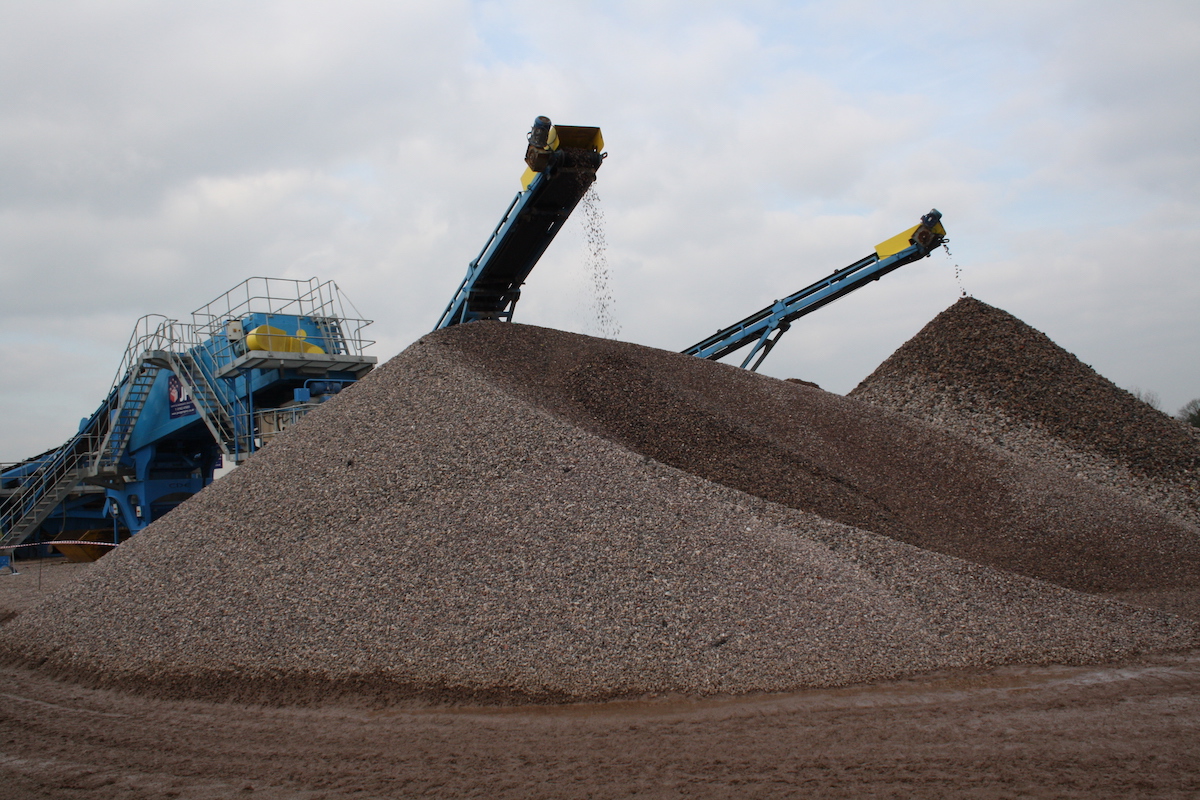
Aggregate refers to a collection of coarse to medium-grained materials used extensively in construction. These materials range from natural elements like sand and gravel to manufactured ones such as crushed stone and recycled concrete. By combining these aggregates with binders like cement or bitumen, professionals create vital construction materials such as concrete, mortar, and asphalt.
Essential Characteristics of Aggregates
The performance and durability of construction materials heavily depend on the quality and properties of the aggregates used. Some of the key characteristics include:
- Size and Gradation: The dimension and distribution of aggregate particles are crucial as they influence the strength, density, and workability of the final mixture.
- Shape and Surface Texture: The physical form and texture impact how aggregates bind with cement or asphalt, affecting the mixture’s overall stability and compactness.
- Density and Specific Gravity: These properties determine the weight and structural load that the aggregate-based material can support.
- Moisture Content: The water content in aggregates affects their mixing behavior and the curing process of concrete or mortar.
- Durability and Abrasion Resistance: Aggregates must withstand environmental factors and mechanical stress without significant degradation.
Types of Aggregates
Understanding the different types of aggregates helps in selecting the right material for specific construction requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the main categories:
Natural Aggregates
Sourced directly from natural environments through processes like mining and quarrying, these aggregates are often used in their raw form. Types include:
- Sand: A fine aggregate composed of tiny grains from eroded rocks. It’s essential in concrete and mortar formulations.
- Gravel: A coarse aggregate of rounded or angular rock fragments. It’s used in concrete mixes and as a reliable base for roads and structures.
- Crushed Stone: This is larger rock fragments crushed into desired sizes, widely used in high-strength concrete and as a base layer for infrastructure.
Manufactured Aggregates
Produced through industrial processes, these aggregates are tailored for specific uses:
- Slag: A by-product of metal smelting, slag aggregates are used in concrete and asphalt for their robustness and thermal properties.
- Synthetic Aggregates: Created from various industrial wastes, these aggregates contribute to sustainable building practices by recycling materials.
Recycled Aggregates
These eco-friendly aggregates come from the demolition of existing structures:
- Crushed Concrete: Salvaged from demolished concrete structures, this aggregate finds a second life in new construction, reducing waste.
- Recycled Asphalt: Old asphalt pavements are processed to create aggregates for new road projects, promoting circular economy principles in construction.
Utilization of Aggregates in Construction
Aggregates have a wide range of applications depending on their types and properties:
- Concrete Production: Aggregates form the bulk of concrete, providing it with structure and volume while influencing its mechanical properties.
- Asphalt Composition: Coarse aggregates are mixed with bitumen to construct durable road surfaces.
- Foundation and Base Layers: Gravel and crushed stone are ideal for creating stable foundations and underlayers for roads and buildings.
- Drainage Systems: Certain aggregates are chosen for their permeability to facilitate effective water drainage in civil projects.
Conclusion
Aggregates are more than mere materials; they are the backbone of the construction industry. Their varied types and properties enable the creation of structures that are both functional and durable. From skyscrapers and highways to bridges and homes, aggregates ensure that our built environment stands the test of time. Whether sourced naturally, manufactured, or recycled, each type of aggregate plays an indispensable role in shaping our world.